Do Most Disc Herniations Mean That Surgery Is Needed?
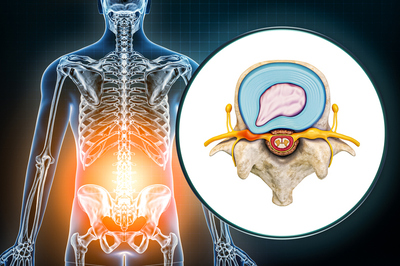 No. In fact, 85% of our patients do not require surgery and respond to non-surgical options. The following tips are often able to alleviate the pain, reduce inflammation, and help the body heal naturally.
No. In fact, 85% of our patients do not require surgery and respond to non-surgical options. The following tips are often able to alleviate the pain, reduce inflammation, and help the body heal naturally.
Strategies for avoiding surgery in cases of disc herniation:
- Rest and avoiding activities that exacerbate the symptoms can be helpful. Bed rest may be recommended for a short period to reduce pressure on the affected disc.
- Over-the-counter medications may be used to manage pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and pain relievers can provide relief.
- A physical therapist can design an exercise program to strengthen the back and core muscles, improve posture, and reduce strain on the spine.
- Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Cold packs are typically used in the acute phase, while heat may be used for chronic pain.
- Chiropractic adjustments can help improve spinal alignment and reduce pressure on the affected disc.
- Acupuncture may provide relief by promoting blood flow and releasing endorphins, which are natural pain relievers.
- Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and adopting proper lifting techniques can prevent further injury and support healing.
- Gentle yoga and stretching exercises can improve flexibility, relieve muscle tension, and promote better posture.
Surgery is typically considered only after these strategies above have not provided significant relief, or if there are severe neurological symptoms like muscle weakness, loss of bladder or bowel control. In these cases, it is important to see an expert healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for a disc herniation.
