Like Horses, Can Humans Get Swayback?
Lordosis
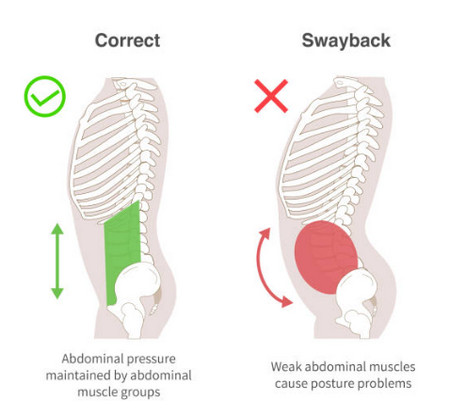
Yes, humans can develop a condition similar to swayback in horses, known as lordosis. Lordosis is characterized by an excessive inward curvature of the lower back (lumbar spine), which can cause the abdomen to protrude and the buttocks to appear more prominent.
In many cases, lordosis can be managed or corrected with physical therapy, exercises to strengthen the core muscles, weight management, and, in some cases, medical treatment. Severe cases might require more specialized medical interventions.
What causes Lordosis?
Lordosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Muscle Imbalances: Weak abdominal muscles and tight lower back muscles can lead to an imbalance, causing the spine to curve more than usual.
- Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can pull the spine forward, increasing the curve in the lower back.
- Poor Posture: Consistently slouching or improper sitting and standing habits can contribute to the development of lordosis.
- Spinal Conditions: Conditions such as spondylolisthesis, where a vertebra slips out of place, or achondroplasia, a form of dwarfism that affects bone growth, can lead to lordosis.
- Pregnancy: The additional weight and changes in the center of gravity during pregnancy can cause a temporary increase in lumbar curvature, known as swayback.
- Congenital or Developmental Issues: Some people may be born with or develop spinal deformities that contribute to lordosis, such as congenital lordosis or Scheuermann’s disease.
- Trauma or Injury: Injuries to the spine or muscles around the spine can lead to changes in curvature as the body tries to compensate.
- Osteoporosis: This condition weakens the bones, making them more susceptible to fractures, which can alter the spine’s curvature.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Arthritis or other inflammatory diseases can affect the spine’s structure and alignment, leading to lordosis.
Again, it is often the case that lordosis can be managed or corrected with physical therapy, exercises to strengthen the core muscles, and/or weight management. However, there are times when more specialized medical interventions are appropriate.
